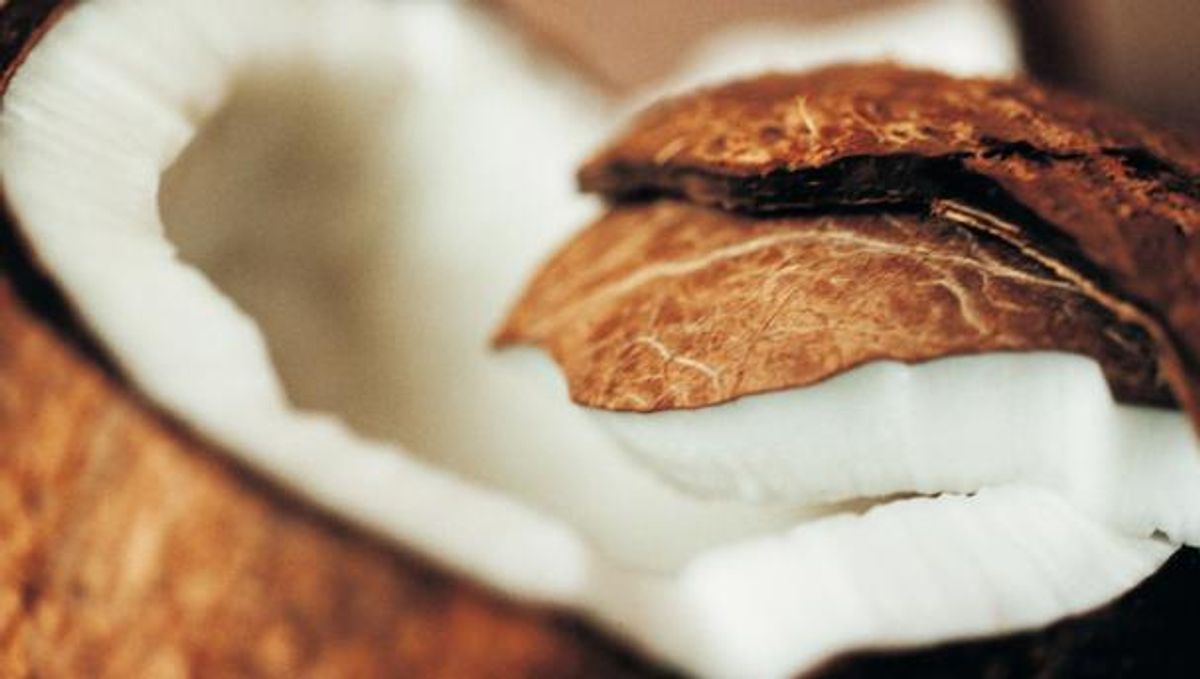
Ever heard of Coconut Testa? No?
Well, here it is!
Coconut Testa is the brown part that covers the coconut kernel (also known as the coconut flesh). The utilization of the Coconut Testa has been limited to animal feed or directly disposed of as a by-product of desiccated coconut or virgin coconut oil. However, multiple researchers have recently discovered that there is more to Coconut Testa!
Coconut Testa is also rich in potassium and have high amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA). It has also been proven to be a natural source of antioxidants such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, tocopherols and tocotrienols than other coconut extracts. These minor nutrient components may act as anti-tumour and anti-aging agents, as well as improves the conditions of degenerative disease such as diabetes, cancer, hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Speaking of diabetes….
Coconut Testa displays a mild α-amylase inhibition but a strong α-glucosidase inhibition which are key features of an effective anti-diabetic agent. The inhibition of α-amylase functions as a strategy to treat carbohydrate intake disorders like diabetes and obesity. In addition, inhibition of α-glucosidase aids in slowing down digestion of carbohydrates, thus lowering glucose levels in the blood. To all the diabetes patients out there, you might want to give this a shot!
Additional Benefits of Coconut Testa Oil:
- Restore moisture for dry & damaged skin
- Treat sunburns
- Stimulate hair growth, prevent pre-mature growth of gray hair
- Can be used as regular consumption
- Contain anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial components
- Gluten-free
- Contain minerals such as manganese, zinc and copper
Are you convinced yet? What are you waiting for?
Try out our Medella’s Wholemeal Coconut Flour or Pacific Series by Medella: Virgin Coconut Oil Plus (VCO+)!
References:
Adekola, KA, Salleh, AB, Zaidan, UH, Azlan, A, Chiavaro, E, Paciulli, M & Marikkar, JMN 2017, ‘Total phenolic content, antioxidative and antidiabetic properties of coconut (Cocos Nucifera L.) testa and selected bean seed coats’, Ital. J. Food Sci., vol. 29, pp. 740-753, <https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/300445846.pdf>.
Appaiah, P, Sunil, L, Krishna, AGG, & Kumar, SG 2016, ‘Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of testa extracts of commercial wet and dry coconuts and cakes’, International Research Journal of Pharmacy, vol. 7, no. 9, pp. 9-13, <http://www.irjponline.com/admin/php/uploads/2551_pdf.pdf>.
Arivalagan, M, Roy, TK, Yasmeen, AM, Pavithra, KC, Jwala, PN, Shivasankara, KS, Manikantan, MR, Hebbar, KB & Kanade, SR 2018, ‘Extraction of phenolic compounds with antioxidant potential from coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) testa and identification of phenolic acids and flavonoids using UPLC coupled with TQD-MS/MS’, LWT, vol. 92, pp. 116-126, <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0023643818301531>.
Bhatia, A, Singh, B, Arora, R & Arora, S 2019, ‘In vitro evaluation of the ꭤ-glucosidase inhibitory potential of methanolic extracts of traditionally used antidiabetic plants’, BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, vol. 19, no. 74, <https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12906-019-2482-z>.
Munduvayalil, Sadhya Coconut Testa Oil, <https://munduvayalil.com/coconut-testa-oil.php#:~:text=Coconut%20Testa%20is%20the%20brown,Powder%20and%20Virgin%20Coconut%20Oil>.